Fehlererkennungsmethoden für Omron-Relais
Release-Zeit:2023-04-21 16:02:21
Fault detection Method One
1. You can first check whether the voltage of the Omron relay is high or low. Generally, the maximum voltage is between 180V and 240V.
Fault detection Method two
2. In addition, when the Omron relay fails, the first thing to check is the external connection of the relay, to see whether the connection of the relay contacts is wrong or broken, falling off or other abnormal phenomena.
Fault detection Method three
3. Next, you can check the power supply circuit of Omron relay and use the meter to test whether the voltage of positive and negative power supplies is the same. If the voltage value measured is the same, it can be inferred that the relay is normal. If the voltage is not a problem, then the power amplifier delay and protection circuit can be carried out.
Fault detection Method four
4. At this time, the Omron relay also needs to measure the power amplifier's final circuit. You can visually check whether there are components burned. Need to be further measured, power amplifier tube emission stage resistance to the ground has DC voltage (normal value is within 0.7V) if there is DC voltage that is generally the power amplifier at the end of the circuit problem, then the treatment method can only replace a power amplifier tube emission stage resistance.
Omron relay note instructions
1. When installing Omron relay, it must not be pushed in too hard, so as not to damage shafting and code plate. The OMRON relay should be gently pushed into the bushing shaft.
2. When using the Omron relay, it is necessary to check whether the plate spring is loose relative to the Omron relay and whether the screw of the relay is loose, so as to avoid some faults and other accidents in the process of operation.
3. Do not randomly connect the terminal between the Omron relay to the wrong, otherwise it is easy to cause the damage of the Omron relay in power-on operation.

-
 202303-03
202303-03MCGS touch screen 485 communication precautions
1. Variablen in der Echtzeitlaufzeit können nicht gleichzeitig Kanäle hinzufügen und Funktionen zum Senden von Daten verwenden.2. Im übergeordneten Gerät der universellen seriellen Schnittstelle ···
-
 202212-29
202212-29Wartungsschritte für Delta-Frequenzumrichter
Zunächst muss bei der Reparatur des Frequenzumrichters geprüft werden, ob das Geräusch beim Betrieb des Motors anormal ist, einschließlich der Frage, ob es beim Betrieb des Motors sensationell ist···
-
 202301-29
202301-29Schneider-Frequenzumrichterstörung und Behandlungsverfahren
A. Kommunikationsmethode:(1) Störung der Strahlung(2) LeitungsstörungB. Methode zur Unterdrückung von StörungenStörsignale, die durch Strahlungsmethoden übertragen werden, werden hauptsächlich ···
-
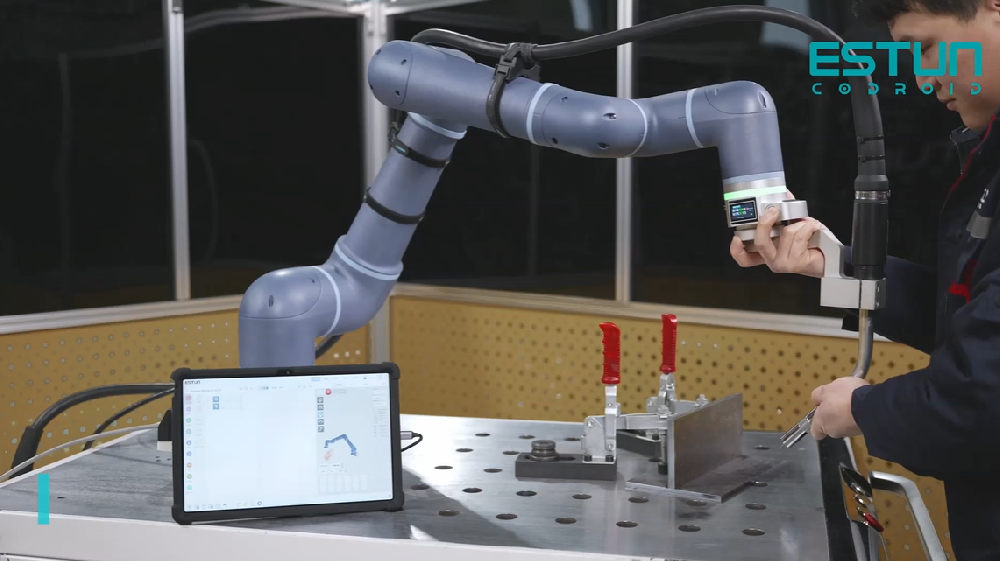 202512-25
202512-25ESTUN Schweißlösungen: Steigerung der Präzision, Effizienz und Flexibilität in der Schweißautomatisierung
Im Bereich des industriellen Schweißens, wo Präzision, Konsistenz und Anpassungsfähigkeit von höchster Bedeutung sind, stellt ESTUN seine modernsten integrierten Schweißlösungen vor. DieseEine u···
-
 202302-15
202302-15Was Symptom hat die Fehlfunktion des WEINVIEW-Touchscreens auf dem Motherboard?
1. Das Motherboard kann Peripheriegeräte nicht erkennen / anzeigen.2. Die Peripheriegeräte funktionieren für einige Sekunden oder länger nicht mehr.3. Ein langsamer Start kann darauf hindeuten, da···



 +8618621383628
+8618621383628 +8613811814778
+8613811814778 info@zhongpingtech.com
info@zhongpingtech.com Gebäude 26, Gemeinde Liyuan, Bezirk Chaoyang, Peking, China
Gebäude 26, Gemeinde Liyuan, Bezirk Chaoyang, Peking, China